Wednesday, April 4, 2012
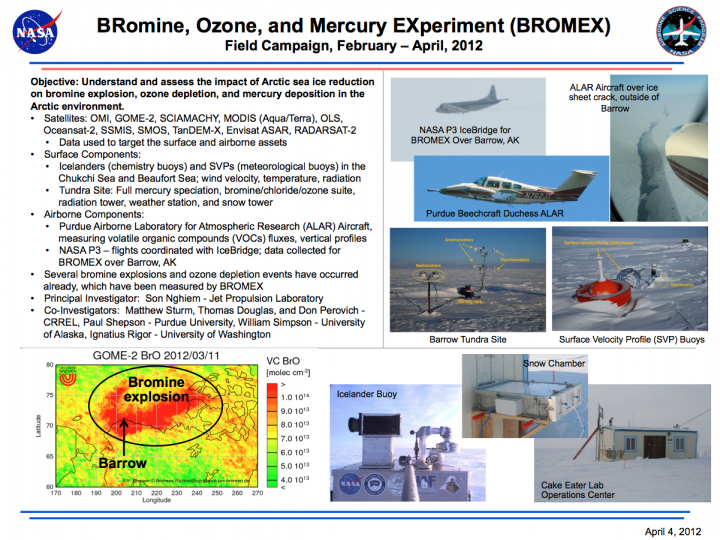
Objective: Understand and assess the impact of Arctic sea ice reduction on bromine explosion, ozone depletion, and mercury deposition in the Arctic environment.
- Satellites: OMI, GOME-2, SCIAMACHY, MODIS (Aqua/Terra), OLS, Oceansat-2, SSMIS, SMOS, TanDEM-X, Envisat ASAR, RADARSAT-2
- Data used to target the surface and airborne assets - Surface Components:
- Icelanders (chemistry bouys) and SCPs (meteorological buoys) in the Chukchi Sea and Beaufort Sea; wind velocity, temperature, radiation
- Tundra Site: Full mercury speciation, bromine/chloride/ozone suite, radiation tower, weather station, and snow tower
- Airborne Components:
- Purdue Airborne Laboratory for Atmospheric Research (ALAR) Aircraft, measuring volatile organic compounds (VOCs) fluxes, vertical profiles
- NASA P3 - flights coordinated with IceBridge; data collected for BROMEX over Barrow, AK
- Several bromine explosions and ozone depletion events have occured already, which have been measured by BROMEX
- Principal Investigator: Son Nghiem - Jet Propulsion Laboratory
- Co-Investigators: Matthew Sturm, Thomas Douglas, and Don Perovich - CRREL, Paul Shepson - Purdue University, William Simpson - University of Alaska, Ignatius Rigor - University of Washington